In this module, you create the custom objects that make up the data model for the conference application.
Login into your Developer Edition account
Click the Setup link (upper right corner)

In the left navigation, select Build > Create > Objects
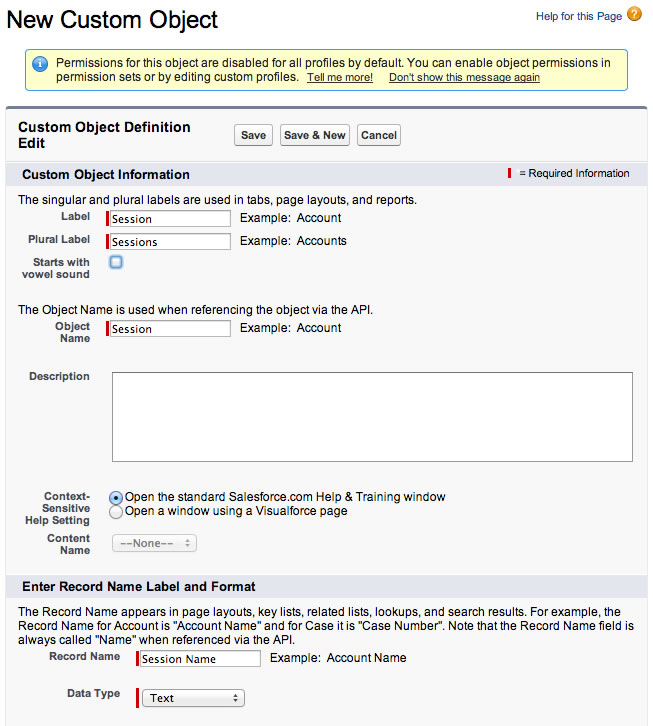
Click New Custom Object, and define the Session object as follows (accept the default values for the properties that are not mentioned below):
Click Save
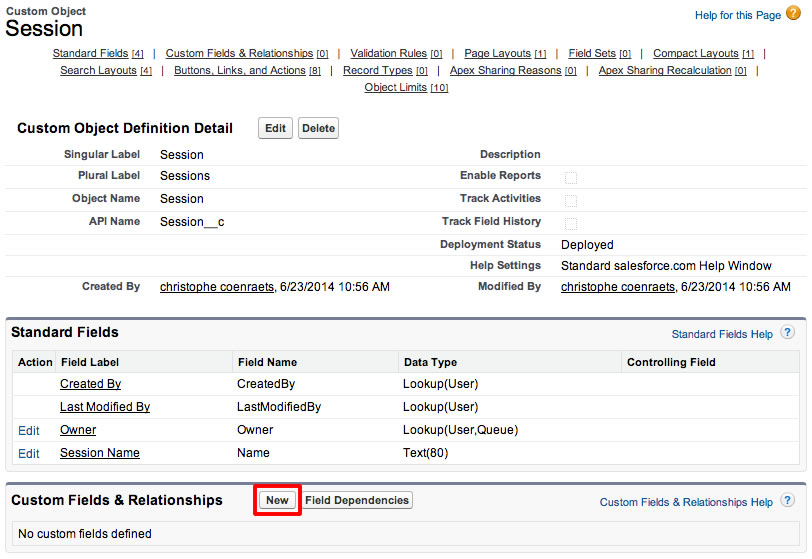
In the Custom Fields & Relationships section, click New
Create a Session Date field defined as follows:
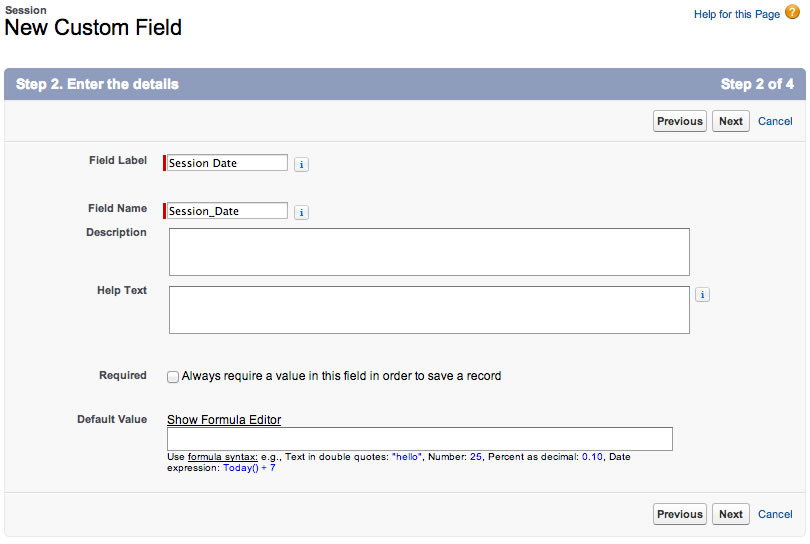
Click Next, Next, Save & New
Create a Description field defined as follows:
Click Next, Next, Save & New
Create a Level field defined as follows:
Click Next, Next, Save
In Setup mode, select Build > Create > Objects
Click New Custom Object, and define the Speaker object as follows (accept the default values for the properties that are not mentioned below):
Click Save
In the Custom Fields & Relationships section, click New, and create a First Name field defined as follows:
Click Next, Next, Save & New
Create a Last Name field defined as follows:
Click Next, Next, Save & New
Create an Email field defined as follows:
Click Next, Next, Save & New
Create a Bio field defined as follows:
Click Next, Next, Save
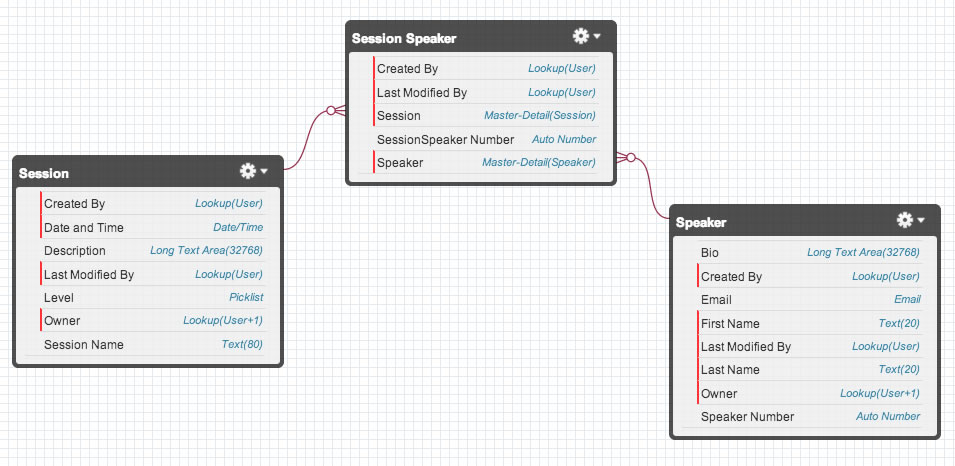
The Session_Speaker object is used to model the many-to-many relationship between Session and Speaker: a session can have one or many speakers, and a speaker can have one or many sessions. This is similar to an associative table in a traditional relational database.
In Setup mode, select Build > Create > Objects
Click New Custom Object, and define the Session_Speaker object as follows:
Click Save
In the Custom Fields & Relationships section, click New, and create a Session field defined as follows:
Click Next, Next, Next, set the Related List Label to "Speakers" and click Save & New
Create a Speaker field defined as follows:
Click Next, Next, Next, set the Related List Label to "Sessions" and click Save
In Setup mode, search for "schema" in the left navigation, and click Schema Builder

Click Clear All
Check Session, Speaker, and Session Speaker
Examine the Conference application data model. Rearrange the objects as needed.